Informal Reading Inventory Independent Instructions Means and Standere
Independent vs. Dependent Variables | Definition & Examples
In research, variables are any characteristics that tin can have on different values, such equally height, age, temperature, or test scores.
Researchers often dispense or measure independent and dependent variables in studies to test cause-and-issue relationships.
- The independent variable is the cause. Its value is contained of other variables in your study.
- The dependent variable is the effect. Its value depends on changes in the independent variable.
Your independent variable is the temperature of the room. You lot vary the room temperature by making it libation for half the participants, and warmer for the other half.
Your dependent variable is math test scores. You mensurate the math skills of all participants using a standardized test and check whether they differ based on room temperature.
What is an independent variable?
An contained variable is the variable y'all manipulate or vary in an experimental study to explore its furnishings. It'due south called "contained" because it's not influenced by any other variables in the study.
Contained variables are too called:
- Explanatory variables (they explain an upshot or outcome)
- Predictor variables (they can exist used to predict the value of a dependent variable)
- Right-hand-side variables (they appear on the correct-hand side of a regression equation).
These terms are especially used in statistics, where you estimate the extent to which an independent variable change can explicate or predict changes in the dependent variable.
Types of contained variables
There are 2 main types of contained variables.
- Experimental independent variables can exist direct manipulated past researchers.
- Field of study variables cannot be manipulated by researchers, simply they can be used to grouping inquiry subjects categorically.
Experimental variables
In experiments, you lot manipulate independent variables direct to run into how they affect your dependent variable. The contained variable is ordinarily practical at different levels to see how the outcomes differ.
You can apply just two levels in order to detect out if an contained variable has an effect at all.
Y'all tin can also employ multiple levels to find out how the contained variable affects the dependent variable.
You take 3 independent variable levels, and each group gets a different level of treatment.
You lot randomly assign your patients to one of the iii groups:
- A low-dose experimental group
- A loftier-dose experimental grouping
- A placebo grouping
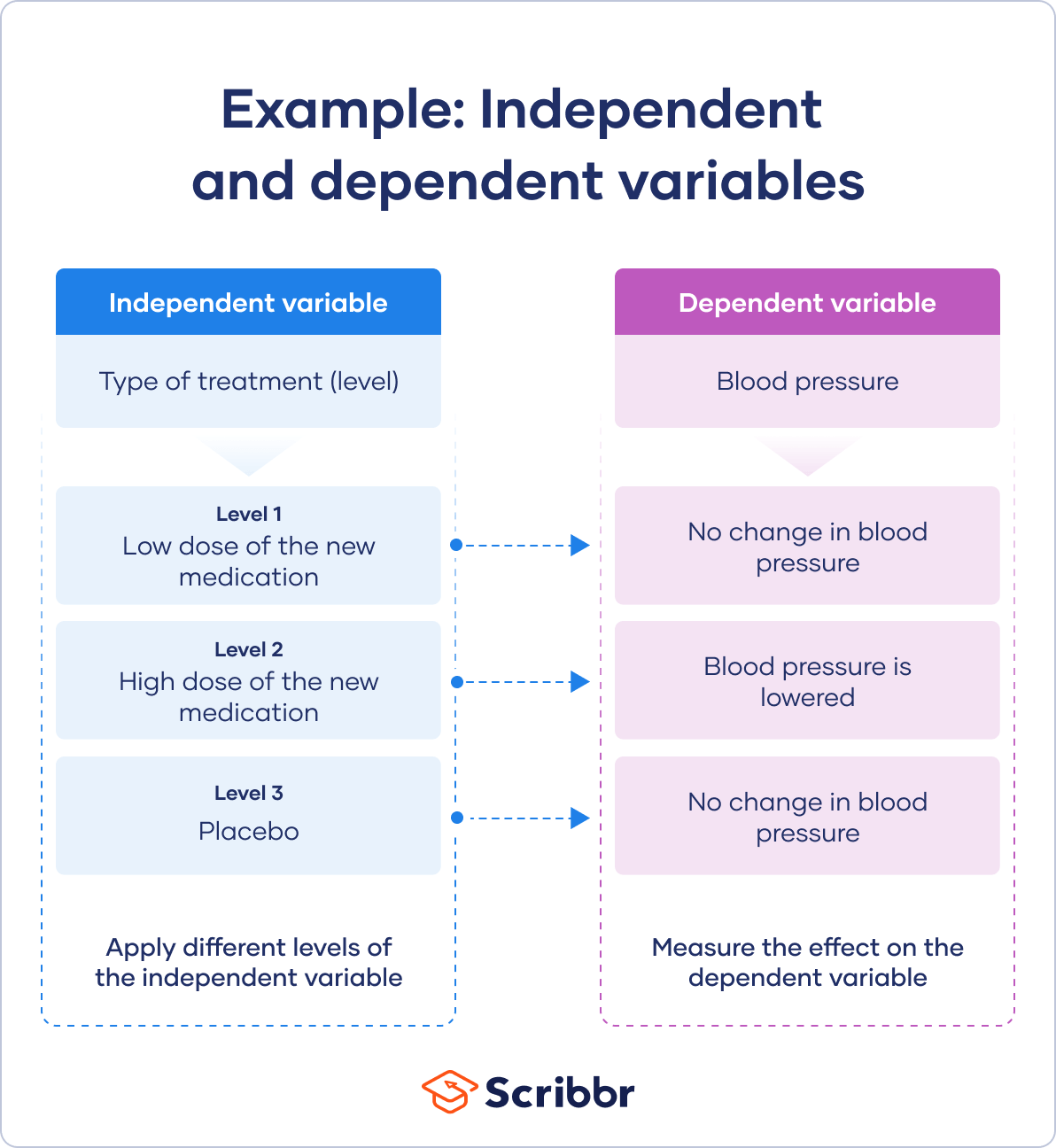
A truthful experiment requires you to randomly assign different levels of an independent variable to your participants.
Random assignment helps y'all command participant characteristics, so that they don't touch your experimental results. This helps yous to have conviction that your dependent variable results come up solely from the independent variable manipulation.
Subject variables
Field of study variables are characteristics that vary beyond participants, and they tin can't be manipulated by researchers. For example, gender identity, ethnicity, race, income, and teaching are all important field of study variables that social researchers treat as contained variables.
It's non possible to randomly assign these to participants, since these are characteristics of already existing groups. Instead, you can create a research design where yous compare the outcomes of groups of participants with characteristics. This is a quasi-experimental design considering in that location's no random consignment.
Your independent variable is a discipline variable, namely the gender identity of the participants. You have 3 groups: men, women and other.
Your dependent variable is the brain activity response to hearing infant cries. You record brain activity with fMRI scans when participants hear infant cries without their awareness.
After collecting data, you bank check for statistically meaning differences betwixt the groups. You find some and conclude that gender identity influences brain responses to baby cries.
What is a dependent variable?
A dependent variable is the variable that changes as a upshot of the independent variable manipulation. It's the event yous're interested in measuring, and it "depends" on your contained variable.
In statistics, dependent variables are also called:
- Response variables (they respond to a alter in another variable)
- Issue variables (they represent the consequence you lot desire to mensurate)
- Left-hand-side variables (they appear on the left-hand side of a regression equation)
The dependent variable is what y'all record later you lot've manipulated the independent variable. You use this measurement data to check whether and to what extent your independent variable influences the dependent variable by conducting statistical analyses.
Based on your findings, you tin estimate the degree to which your independent variable variation drives changes in your dependent variable. You lot can also predict how much your dependent variable will change as a result of variation in the independent variable.
Identifying independent vs. dependent variables
Distinguishing between independent and dependent variables can exist tricky when designing a complex written report or reading an academic paper.
A dependent variable from ane study can be the contained variable in some other study, so it's important to pay attention to research pattern.
Here are some tips for identifying each variable type.
Recognizing contained variables
Use this listing of questions to check whether you're dealing with an contained variable:
- Is the variable manipulated, controlled, or used equally a subject grouping method by the researcher?
- Does this variable come before the other variable in time?
- Is the researcher trying to sympathise whether or how this variable affects another variable?
Recognizing dependent variables
Check whether you're dealing with a dependent variable:
- Is this variable measured as an issue of the written report?
- Is this variable dependent on another variable in the report?
- Does this variable get measured only after other variables are altered?
Independent and dependent variables in enquiry
Contained and dependent variables are generally used in experimental and quasi-experimental research.
Here are some examples of inquiry questions and corresponding independent and dependent variables.
| Research question | Independent variable | Dependent variable(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Practice tomatoes grow fastest nether fluorescent, incandescent, or natural light? |
|
|
| What is the upshot of intermittent fasting on claret carbohydrate levels? |
|
|
| Is medical marijuana effective for pain reduction in people with chronic pain? |
|
|
| To what extent does remote working increase job satisfaction? |
|
|
For experimental information, yous analyze your results by generating descriptive statistics and visualizing your findings. Then, you select an appropriate statistical exam to test your hypothesis.
The type of test is determined past:
- your variable types
- level of measurement
- number of contained variable levels.
Yous'll often utilise t tests or ANOVAs to analyze your data and answer your research questions.
Visualizing independent and dependent variables
In quantitative research, it's practiced practice to use charts or graphs to visualize the results of studies. Generally, the independent variable goes on the 10-centrality (horizontal) and the dependent variable on the y-axis (vertical).
The type of visualization you employ depends on the variable types in your research questions:
- A bar chart is ideal when yous accept a categorical independent variable.
- A scatter plot or line graph is all-time when your independent and dependent variables are both quantitative.
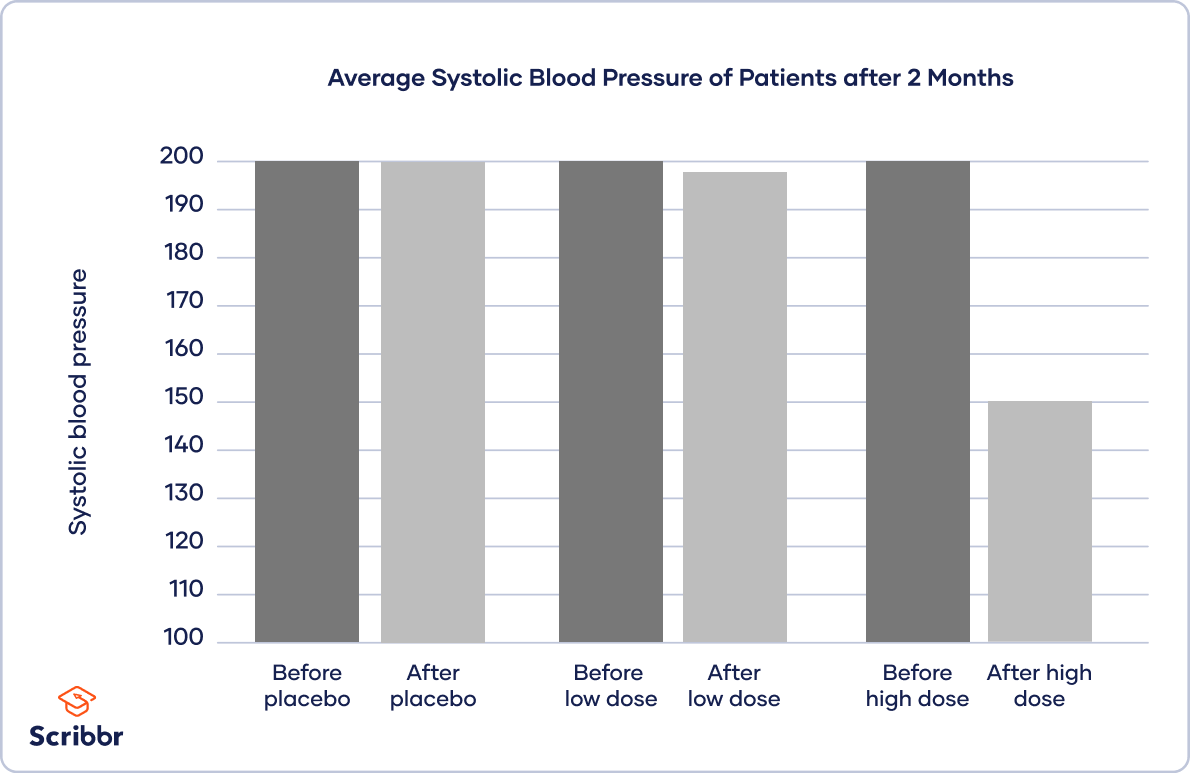
To inspect your data, you place your independent variable of treatment level on the x-centrality and the dependent variable of blood pressure on the y-axis.
You plot bars for each treatment group before and after the treatment to show the difference in blood pressure.
Based on your results, you note that the placebo and low-dose groups show petty difference in blood pressure, while the high-dose group sees substantial improvements.
Frequently asked questions about contained and dependent variables
- What's the definition of an contained variable?
-
An contained variable is the variable you lot manipulate, control, or vary in an experimental study to explore its furnishings. It's called "independent" considering it'due south not influenced by any other variables in the study.
Independent variables are also called:
- Explanatory variables (they explain an issue or outcome)
- Predictor variables (they can be used to predict the value of a dependent variable)
- Right-mitt-side variables (they appear on the right-hand side of a regression equation).
- What's the definition of a dependent variable?
-
A dependent variable is what changes as a result of the independent variable manipulation in experiments. It'southward what you lot're interested in measuring, and it "depends" on your independent variable.
In statistics, dependent variables are besides called:
- Response variables (they answer to a modify in another variable)
- Effect variables (they represent the outcome you want to measure out)
- Left-mitt-side variables (they appear on the left-hand side of a regression equation)
- Tin I include more than than i independent or dependent variable in a study?
-
Yeah, simply including more than one of either type requires multiple research questions.
For example, if you are interested in the effect of a diet on wellness, you tin use multiple measures of health: blood sugar, blood force per unit area, weight, pulse, and many more. Each of these is its own dependent variable with its own research question.
You could too choose to expect at the issue of practise levels as well as diet, or fifty-fifty the additional event of the ii combined. Each of these is a separate contained variable.
To ensure the internal validity of an experiment, you should only change one contained variable at a time.
Is this article helpful?
You have already voted. Thanks :-) Your vote is saved :-) Processing your vote...
Source: https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/independent-and-dependent-variables/
ارسال یک نظر for "Informal Reading Inventory Independent Instructions Means and Standere"